Introduction to Curriculum Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's ever-changing educational landscape, 80% of students globally face a risk of falling behind intellectually (Wilkerson, 2020). This could affect their future income and growth. In light of this pressing issue, we invite you to delve into our blog, "Introduction to Curriculum Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide." We'll show you how Curriculum Mapping can be a game-changer, aligning learning goals with results to ensure students stay on the path to success.
But what precisely does curriculum mapping entail? And what is the source of the attention it's currently capturing? Join us as we explore the importance of Curriculum Mapping in today's education. We'll discuss how it can bridge the gap between what students learn and what they should achieve, ultimately paving the way for a more prosperous future for students everywhere.
Understanding curriculum mapping - Meaning and Significance
This term refers to the process of systematically documenting what is being taught (the curriculum) in an educational program. It involves identifying the content, skills, and concepts that students are expected to learn over a specific period. Curriculum mapping provides a visual representation of the curriculum, often using tools like charts or software. Understanding curriculum mapping's significance is crucial in recognizing its role in improving education. Here are some key reasons why curriculum mapping is highly significant:
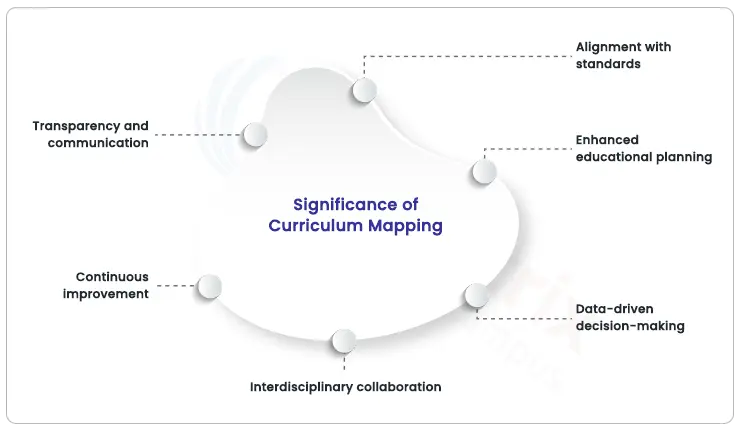
Alignment with standards:
Curriculum mapping ensures that the educational program aligns with educational standards and goals set by educational authorities. This alignment is essential for maintaining quality education and accountability.
Enhanced educational planning:
Educators use curriculum maps to plan their instructional activities more effectively. It helps in creating coherent lesson plans, units, and teaching strategies that lead to better student learning outcomes.
Data-driven decision-making:
Curriculum mapping provides a structured framework for data collection and analysis. Educators can use this data to identify areas of improvement, assess student progress, and make informed decisions about instructional adjustments.
Interdisciplinary collaboration:
Curriculum mapping fosters collaboration among educators within an institution. It promotes the sharing of best practices, ensuring consistency in teaching approaches and a more cohesive learning environment.
Continuous improvement:
Curriculum maps are dynamic documents that can be updated and refined over time. This allows for ongoing improvements to the curriculum to reflect changes in educational needs, advances in pedagogy, and emerging knowledge.
Transparency and communication:
Curriculum mapping promotes transparency in educational processes. It helps educators, students, and parents understand what is being taught and why, enhancing communication and accountability.
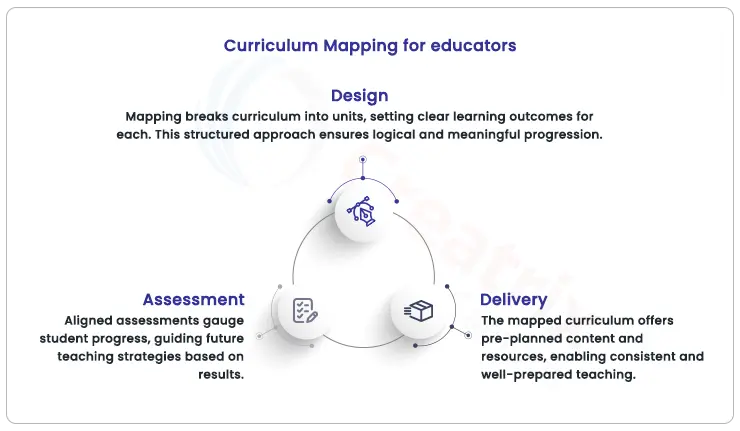
Curriculum mapping as empowering educators
Curriculum mapping empowers educators in three key areas: design, delivery, and assessment.
The Core Components of Curriculum Mapping
A curriculum map is a mosaic of critical elements that converge to craft a seamless educational experience. These essential components include
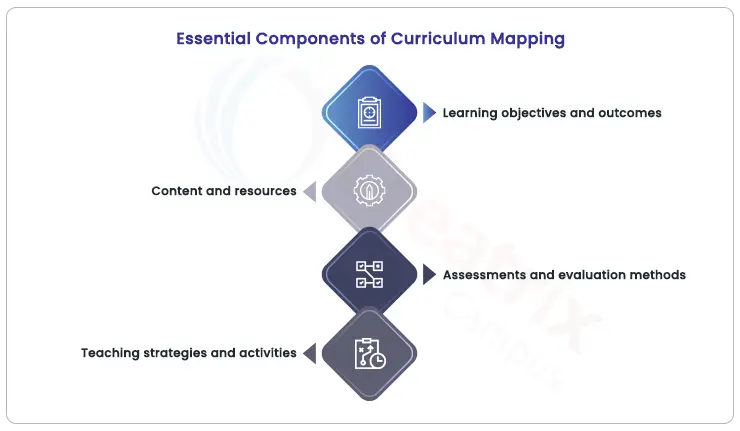
Learning objectives and outcomes:
The foundation of any curriculum, learning objectives set clear goals for what students should understand and achieve. They define the skills, knowledge, and competencies students will acquire throughout the curriculum.
Content and resources:
Curriculum maps outline the specific content that will be covered, from textbooks to multimedia resources. These materials are selected to align with the learning objectives and facilitate effective teaching.
Assessments and evaluation methods:
Assessment strategies are integrated to measure students' mastery of the learning objectives. This includes quizzes, exams, projects, and other evaluative methods that provide insights into student progress and guide instruction adjustments.
Teaching strategies and activities:
Educators employ a range of teaching methods to engage students and facilitate effective learning. These strategies include lectures, discussions, hands-on activities, group projects, and more, ensuring diverse and meaningful learning experiences.
These components collaborate synergistically to shape a comprehensive educational plan, ensuring alignment as learning objectives guide content selection, teaching methods, and assessment tools, guaranteeing congruence with desired educational outcomes. The curriculum map provides a structured progression of content and activities, facilitating a logical and incremental accumulation of knowledge and skills for students. Assessments play a pivotal role in evaluating students' attainment of learning objectives, consequently validating the curriculum's effectiveness.
Ongoing evaluation of both student performance and the curriculum itself enables adaptable adjustments in teaching approaches, content coverage, and assessment strategies to enhance learning outcomes.
Lastly, a well-structured curriculum map fosters coherence by interconnecting all its elements, resulting in a harmonious learning experience, which aids educators in maintaining consistency and staying on target with educational goals.
Benefits of Curriculum Mapping
Curriculum mapping is not just a systematic process; it's a catalyst for transformative educational outcomes. This methodology brings a plethora of benefits that extend to educators, students, and institutions alike.
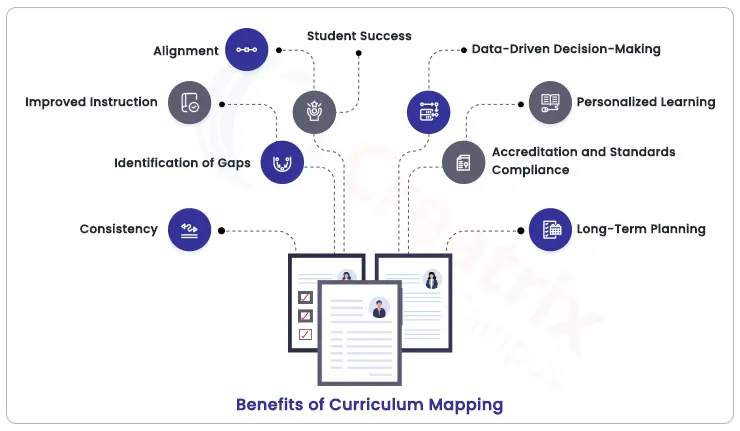
Enhanced alignment with learning goals
Curriculum mapping ensures that every facet of the educational experience, from content to assessments, aligns seamlessly with predefined learning objectives. This alignment leads to a focused and purposeful learning journey, where every lesson contributes to the broader educational goals. As a result, students acquire the targeted knowledge and skills necessary for success.
Improved instructional strategies
With a well-structured curriculum map, educators gain insights into the most effective instructional strategies for each learning objective. This allows for strategic selection of teaching methods, fostering engagement and deepening students' understanding. Varied strategies cater to diverse learning styles, making the learning experience more inclusive and effective.
A clear progression of skills and knowledge
Curriculum mapping introduces a clear roadmap for the progressive acquisition of skills and knowledge. Each unit builds upon the previous one, creating a scaffolded learning experience that ensures students have a solid foundation before moving on to more complex topics. This gradual progression enhances retention and mastery.
Data-driven decision-making
One of the most significant advantages of curriculum mapping is its data-driven nature. Assessment results provide valuable insights into students' strengths and areas that need improvement. Educators can use this information to tailor their teaching methods, offer targeted interventions, and refine the curriculum itself, enhancing overall educational effectiveness.
Facilitated communication among educators
Curriculum mapping fosters collaboration among educators. By having a shared understanding of the curriculum's components and objectives, educators can seamlessly exchange ideas, share resources, and coordinate efforts. This collaborative environment enriches the teaching process and encourages the cross-pollination of innovative teaching practices.
Types of Curriculum Maps
In the realm of curriculum mapping, variety is the spice that adds depth and richness to educational planning. Different types of curriculum maps offer unique perspectives, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing teaching and learning experiences. Let's embark on a journey through the various types of curriculum maps and unveil their distinctive roles.
1. Vertical curriculum maps:
Bridging across grade levels Vertical curriculum maps extend their focus beyond a single grade level, presenting a panoramic view of how learning objectives progress over time. These maps ensure alignment and coherence in education, as concepts build upon each other seamlessly. For instance, a vertical curriculum map for mathematics could track how foundational math skills are developed and expanded upon from elementary to high school levels. This type of map is invaluable for educational institutions seeking to ensure that learning outcomes are consistently achieved as students advance through different stages of their education.
2. Horizontal curriculum maps:
Unifying within a grade level or subject While vertical maps span grades, horizontal curriculum maps zoom in to provide clarity and unity within a specific grade level or subject. These maps promote consistency by aligning learning objectives, content, and assessments across different educators teaching the same grade or subject. An example would be a horizontal curriculum map for a high school biology class, where all instructors ensure that their teaching converges on the same set of objectives and topics. This type of map is especially useful for fostering uniformity in classroom experiences and assessment standards.
3. Concept maps:
Illuminating interconnections Concept maps transcend linear progression, focusing instead on the intricate connections between concepts. They visually represent how ideas link together, fostering a deeper understanding of subject interdependencies. For instance, a concept map in history could showcase how historical events, figures, and ideologies are interwoven, providing students with a holistic view of the subject's complexity. Concept maps are particularly beneficial for promoting critical thinking and helping learners see the bigger picture
The Curriculum Mapping Process
Creating a curriculum map is akin to designing a blueprint for a successful educational journey. It's a strategic process that involves several crucial steps, each contributing to a comprehensive and cohesive learning experience. Let's delve into the intricacies of the curriculum mapping process and uncover how these steps work together.
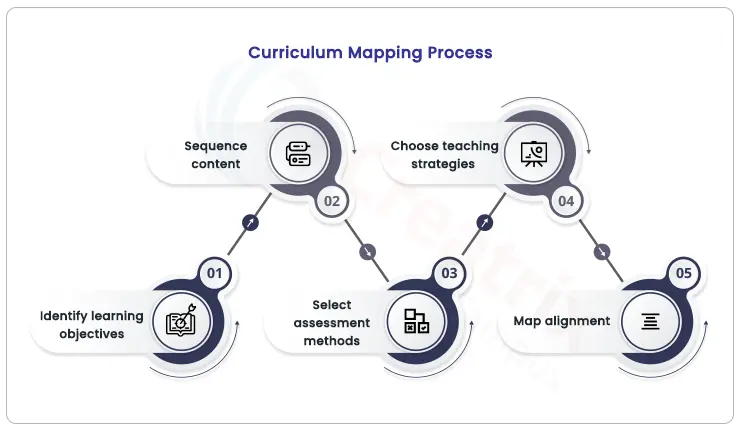
1. Identify learning objectives:
Defining the educational destination At the heart of curriculum mapping are learning objectives. These objectives outline what students are expected to learn and accomplish. They serve as the North Star, guiding the entire educational experience. For instance, in a science curriculum, learning objectives might include understanding key scientific concepts, conducting experiments, and analyzing data.
2. Sequence content:
Building a logical pathway Once learning objectives are defined, the next step is to sequence the content in a logical order. This means arranging topics and skills in a way that ensures a smooth progression of complexity and difficulty. This sequencing helps students build a solid foundation before moving on to more advanced concepts, creating a scaffolded learning journey.
3. Select assessment methods:
Measuring learning outcomes Assessment methods determine how learning outcomes will be evaluated. Educators choose assessments that align with the learning objectives and accurately measure students' comprehension. This might involve quizzes, projects, presentations, or exams. Effective assessment methods provide insights into students' progress and guide instructional adjustments.
4. Choose teaching strategies:
Tailoring Instruction to Objectives Teaching strategies are the tools educators use to convey information and engage students. These strategies should align with the learning objectives and cater to various learning styles. For instance, if the objective is to foster critical thinking, teaching strategies might involve class discussions, problem-solving activities, and hands-on experiments.
5. Map Alignment:
Ensuring consistency and coherence Mapping alignment is the process of checking that all components of the curriculum map work harmoniously. This means confirming that learning objectives match the content, assessment methods align with learning objectives, and teaching strategies complement both. This alignment ensures that the curriculum map is cohesive, coherent, and purposeful.
Tools and Technology for Curriculum Mapping
Technology acts as a catalyst, elevating the curriculum mapping process from static planning to dynamic collaboration. It allows educators to create, visualize, and adapt curriculum maps with precision and ease. The benefits are manifold, from reducing administrative burdens to facilitating data-driven decision-making. Moreover, technology fosters interconnectivity among educators, leading to enhanced communication and deeper exchange of ideas.
Curriculum Mapping Software Features
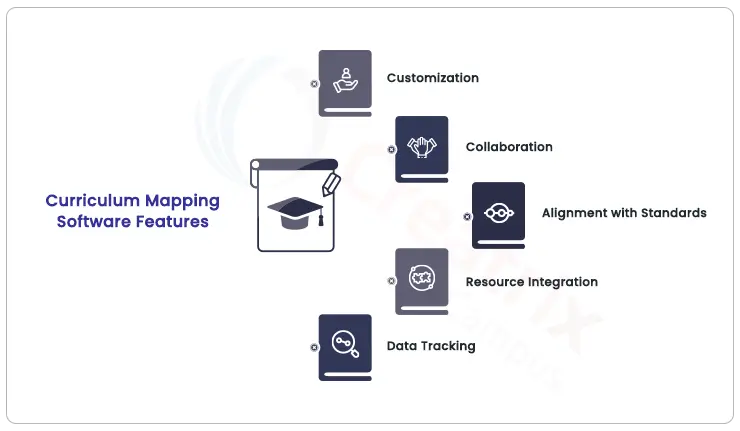
Customization: These tools provide templates that educators can tailor to their specific needs, ensuring that curriculum maps align perfectly with their educational goals.
Collaboration: Technology enables real-time collaboration, allowing multiple educators to work on the same map simultaneously, fostering a rich exchange of insights.
Alignment with Standards: Many tools offer the ability to align curriculum maps with educational standards, ensuring that learning objectives meet predefined benchmarks.
Resource Integration: These platforms often allow educators to incorporate multimedia resources, ensuring that content is enriched and varied.
Data Tracking: Technology allows for the tracking of student progress and assessment results, aiding data-driven decision-making for instructional adjustments.
Overcoming Challenges in Curriculum Mapping
In the realm of curriculum mapping, educators often encounter challenges that can impede the smooth creation and implementation of effective educational plans. However, armed with practical strategies, these challenges can be transformed into opportunities for growth and innovation. Let's delve into some common challenges and explore strategies to overcome them.
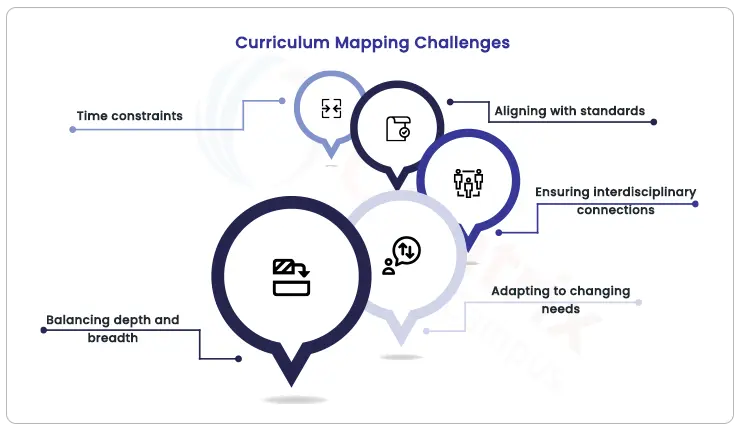
1. Time constraints: Crafting efficiency in mapping
Challenge: Educators frequently find themselves grappling with time constraints due to various responsibilities, leaving limited room for comprehensive curriculum mapping.
: Prioritize and chunk the mapping process. Break it down into manageable segments, focusing on one component at a time. Allocate specific time slots for curriculum planning and utilize tools that streamline the process. Collaborate with fellow educators to share the workload and gather diverse insights, saving time while enhancing the quality of the curriculum map.
2. Aligning with standards: Bridging the gap
Challenge: Aligning curriculum maps with educational standards can be a complex task, requiring meticulous attention to detail.
Strategy: Start with a clear understanding of the standards you need to align with. Break down the standards into specific learning objectives and build your curriculum map around these objectives. Utilize mapping software that offers alignment features to make the process smoother. Regularly review your curriculum map against the standards to ensure ongoing alignment.
3. Ensuring interdisciplinary connections: Fostering holistic learning
Challenge: Integrating various subjects and creating meaningful interdisciplinary connections can be challenging, but it enriches the educational experience.
Strategy: Collaborate with educators from other disciplines to identify natural intersections between subjects. Map out opportunities for cross-disciplinary activities or projects that emphasize real-world connections. Use concept maps to visually represent how concepts from different subjects intertwine. This not only deepens students' understanding but also encourages them to view knowledge holistically.
4. Adapting to changing needs: Flexibility for growth
Challenge: Educational landscapes are ever-evolving, and curriculum maps must adapt to meet changing needs.
Strategy: Embrace flexibility in your curriculum mapping approach. Create maps that are dynamic rather than static documents. Regularly assess student progress and solicit feedback from students and colleagues. Use this information to make necessary adjustments to your curriculum map, ensuring that it remains relevant and effective.
5. Balancing depth and breadth: Navigating content selection
Challenge: Determining what content to include and what to omit can be a balancing act, especially when trying to strike the right balance between depth and breadth.
Strategy: Focus on essential concepts that align closely with your learning objectives. Avoid overloading the curriculum with excessive content. Prioritize depth over breadth, ensuring that students have a solid understanding of fundamental concepts before delving into broader topics. Consider revisiting your curriculum map periodically to fine-tune content choices based on student engagement and outcomes.
Curriculum Mapping and Educational Improvement
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, the pursuit of excellence is a journey without end. Curriculum mapping emerges as a guiding star in this quest, providing a dynamic framework for continuous improvement that enhances the overall educational experience. Let's explore how curriculum mapping contributes to this ongoing journey of refinement.
1. Data-driven adjustments:
Honing through insights Curriculum mapping is inherently data-driven. Assessment results, student performance, and feedback from educators provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the curriculum. By analyzing this data, educators can identify areas where students are excelling and those that require further attention. This information guides adjustments in teaching strategies, content delivery, and assessment methods. As a result, the curriculum becomes a living entity that evolves to meet the ever-changing needs of students.
2. Identifying areas for enhancement:
Nurturing growth Curriculum mapping acts as a magnifying glass, spotlighting both strengths and weaknesses in the educational plan. Through this process, educators can identify areas where enhancements are needed. Whether it's refining learning objectives, updating content to reflect current trends, or revising assessments for greater accuracy, curriculum mapping provides a structured mechanism to target these improvements. It allows educators to address gaps and misconceptions, ensuring that students receive a comprehensive and effective learning experience.
3. Aligning with changing educational goals:
Staying relevant Educational goals are not static; they evolve to align with the demands of a changing world. Curriculum mapping enables educators to seamlessly adapt to these changes. By revisiting and updating the curriculum map, educators can ensure that learning objectives remain in harmony with shifting educational priorities. This alignment ensures that students are equipped with the most relevant knowledge and skills, preparing them to thrive in a rapidly transforming global landscape.
Conclusion
As you reflect on our journey, it becomes clear that curriculum mapping isn't just a concept; it's a roadmap that leads to educational success. It empowers educators to design purposeful learning experiences, propelling students toward holistic growth and mastery.
Explore the possibilities with Creatrix Campus Curriculum Management with robust Curriculum Mapping Features
Curriculum management software from Creatrix Campus is a cutting-edge solution that empowers educational institutions to streamline and enhance their curriculum development and management processes. What sets it apart is its robust curriculum mapping features, which play a pivotal role in shaping a modern and effective educational experience. Here's a closer look at what you can expect from Creatrix Campus's curriculum management software with robust curriculum mapping features:
Efficient Curriculum Organization:
Creatrix Campus allows educators to efficiently organize their curriculum. It provides a structured framework for defining learning objectives, selecting educational resources, and arranging content in a logical sequence.
Alignment with Educational Standards:
The software ensures that curriculum components align seamlessly with educational standards and objectives. This alignment is crucial for maintaining educational quality and relevance.
Visual Curriculum Mapping:
One of the standout features is its visual curriculum mapping capabilities. Educators can create clear and intuitive visual representations of their curriculum, making it easier to understand and manage.
Assessment Integration:
Curriculum mapping within Creatrix Campus includes tools for integrating assessments. This means that educators can plan when and how assessments will be conducted to gauge student progress and achievement of learning objectives.
Data-Driven Insights:
The software provides valuable data and insights into curriculum effectiveness. Educators can analyze student performance data to identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions.
Collaboration and Sharing:
Creatrix Campus encourages collaboration among educators and stakeholders. Curriculum maps can be easily shared and discussed, fostering a collaborative approach to curriculum development and refinement.
Adaptability:
The robust curriculum mapping features are designed to be adaptable. As educational goals and standards evolve, educators can make necessary adjustments to the curriculum to stay current.
Reporting and Documentation: The software facilitates comprehensive reporting and documentation of curriculum-related activities. This documentation is invaluable for accreditation processes and quality assurance.



