How to Use Interactive Pedagogical Tools Effectively During COVID-19

COVID-19 happened without any warnings. At the unprecedented rate that the world is moving forward, students need to navigate and catch up with the complexities of society. There is more and more rush for online interactive pedagogical tools. Higher ed institutions are trying to grab the best teaching and learning approaches that propel the “new generation” learners. Let us get into the list of pedagogical tools for teaching that is currently available and explore how Creatrix Campus contributes to this new form of obtaining pedagogical skills.
What are pedagogical tools?
Pedagogy tools are instructional resources that are used to facilitate and enhance the teaching and learning process. These tools can help educators to design effective teaching strategies and create engaging and interactive learning experiences for students.
There is no limit to what could be a pedagogical tool. It’s totally up to the faculty and the student to make the connection between the concepts, facts, and tools learned. While modern pedagogical tools vary by person-to-person, age, level of education, and situation, virtually anything can be a pedagogical tool in the right circumstances.
Some of the traditional pedagogical tools include textbooks, handouts, microscopes, worksheets, hand-on-models, etc. In the present day, due to technological advancement, a computer, laptops, websites, and mobile app devices could be online pedagogical tools. Some common examples of pedagogy tools include:
- Learning management systems (LMS): LMS is a software application that provides a centralized platform for managing and delivering learning content, tracking student progress, and facilitating communication and collaboration.
- Interactive whiteboards: Interactive whiteboards allow educators to display and manipulate digital content, such as videos, images, and interactive activities, in the classroom.
- Educational software: Educational software is designed to provide interactive and engaging learning experiences for students. This can include gamification, simulations, and virtual reality tools.
- Collaborative tools: Collaborative tools allow students to work together on projects, share resources, and communicate with each other. Examples include Google Docs, online forums, and wikis.
- Assessment tools: Assessment tools can help educators evaluate student progress and understanding of the subject matter. This can include quizzes, surveys, and digital portfolios.
Overall, pedagogy tools can help educators create a more engaging and interactive learning environment, facilitate communication and collaboration among students, and provide more personalized and effective learning experiences.
Need for 21st-century online pedagogical tools
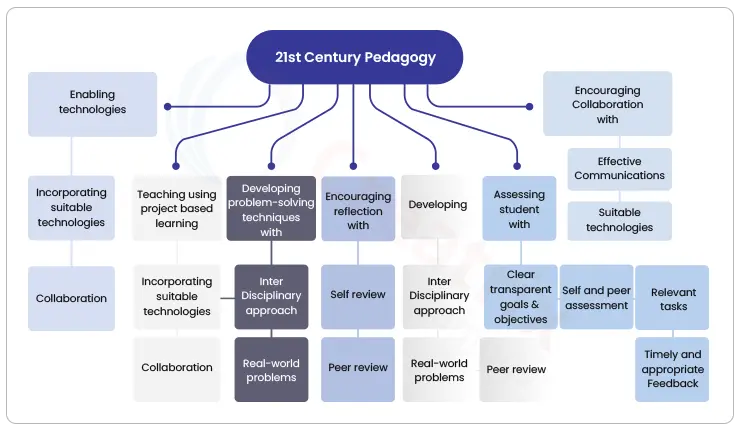
Modern learners need to sift through tons of information. Hence 21st-century pedagogy should focus on several core components of modern learning like critical thinking, technology, project-based learning, metacognition (reflection), and problem-based learning. It should,
- Teach and develop thinking skills
- Encourage collaboration with technologies
- Enable technologies to collaborate and brainstorm
- Assess students with self & peer assessment, appropriate tasks & feedback
- Develop problem-solving using real-world problems
- Teach using project-based learning and collaboration
- Develop media, technological, & information fluency
- Encourage reflection with peer/self-review
Pedagogy in Teaching Education
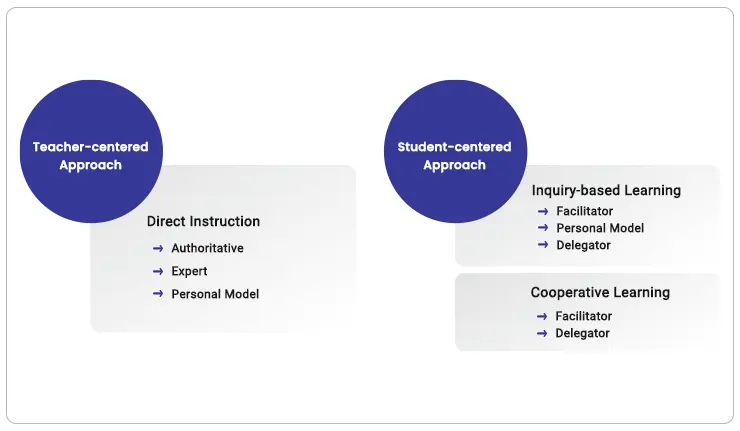
Pedagogy in education takes two important forms. It could be teacher-centered or learner-centered and could either take a low or high-tech approach. Let’s get into their details.
Teacher-centered & Learner-centered approach
While teacher-centered learning concentrates on direct instruction from teachers through classroom lectures, student-centered learning allows students to be active participants in their learning courses.
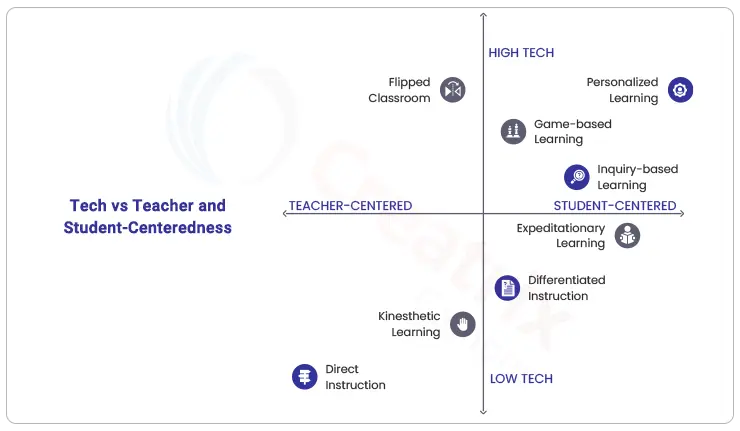
High-tech approach to pedagogy
The advancements in online teaching have propelled a high-tech approach to learning. With digital transformation, educators rely on tablets, computers, and software to teach and evaluate. The high-tech approach to pedagogy is achieved through;
- Higher Education virtual software
- Online learning through external integration (G Suite, Docs, Sheets, Classroom, Drive, and Calendar)
- Tablets/laptops/Mobile learning
Low-Tech approach to learning
On the contrary, the low-tech approach refers to the traditional way of teaching using worksheets, projects, hands-on activities, and case studies. Students learn in the classroom rather than in the virtual world. In this way, the faculty’s presence is essential for efficient interaction to happen.
Each of the above approaches can have its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore for ultimate learning to happen, a combination of pedagogical avenues should be created.
Pedagogy in Learning
According to Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences, each student is unique and faculty should have a differentiated approach to dealing with him. She/he has to deal with a range of pedagogy tools to balance their understanding well.
Here are six important learning styles of Gartner through which students learn.
- Interpersonal and Intrapersonal: While the former style of learners is intuitive and comfortable with relationships, the latter is too reflective and contemplative.
- Visual-Spatial: This kind of learner are always good at figuring out pictures, maps, puzzles, directions, etc
- Linguistic-Verbal: Those who are good at speaking and writing
- Logical-Mathematical: Includes problem solvers, who are good at numbers and arithmetic
- Musical: They appreciate music and rhythm
- Bodily-Kinesthetic: Those who are best at hand-eye coordination
What are the 5 pedagogical approaches?
There are five most important pedagogical approaches to boost student engagement.
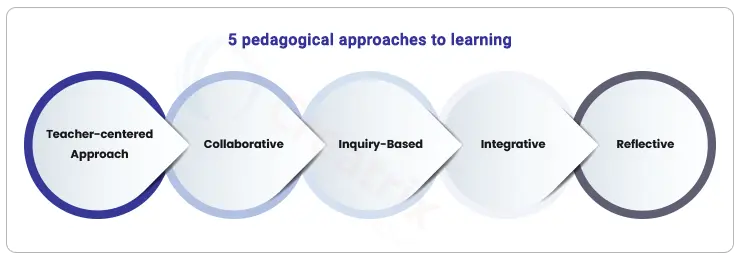
1. Constructivist: An approach that has learners actively involved in learning. They try to construct knowledge, in contrast, to passively receiving it from a facilitator.
2. Collaborative: In this approach, the learners learn in groups, share their experiences, experiment, and create a co-learning environment.
3. Inquiry-Based: The inquiry-based approach is active learning where learners probe each other, discuss problems and scenarios, pose questions, and try to solve them. Its problem-based and project-based learning fits in this category.
4. Integrative: This approach allows students to connect what they learn with the real world. The approach makes learning more meaningful and students improve their subject knowledge too well.
5. Reflective: The practice fosters self-learning, self-observation, and self-evaluation. The faculty does it with the help of projects, lessons, and assessments.
What are some examples of pedagogy?
- Think-pair-share
- Discussion forums
- Flipped learning
- Ad Hoc debates, meetings, polling
- Groups discussion
- Collaboration and sharing
- Teaching by real-world examples within the classroom
What are the types of pedagogical tools used by teachers during Covid 19?
In the current scheme of things, the most commonly discussed question is, “How do I keep students engaged?” With virtual learning, more and more faculty are concerned about ways to engage students. The Grattan Institute's report says that a total of 40% of students are often disengaged in a classroom. If this is the case with classroom learning, imagine an online learning environment.
With the pedagogical tools for teaching, higher education institutions can develop a culture of learning, create openness and trust, and allows students to create, innovate, share ideas, and resources, engage better, self-reflect, improve, and peer review. Here are some of the modern research-based, online pedagogical tools.
Game-based learning or gamification
Games could be a powerful way to create problem-solving skills, creativity, communication, and cooperation among students. They are built on rapid and immediate feedback with students being awarded points, badges, stickers, etc. Students better engage with gamification as they fail, persevere, solve, and overcome the given situation. Modern-day LMSs come with a Gamification feature that attracts most higher education institutions these days.
Flipped Learning
Flipped learning has both the benefits of traditional learning and modern e-learning. This model of reciprocal teaching creates a self-learning space, allowing students to apply concepts and engage better.

With the faculty being aware of the students who have prepared well before the others, she can give tailored attention, and plan out lessons in a way it suits them better. Thus flipped classroom fosters a deeper understanding and creates a better learning experience for students.
Blended learning
This pedagogy blends both online and offline learning in the form of face-to-face instruction, assessments, online games, research, group activities, visual material, group activities, etc. With technology-assisted teaching and learning, students have easy access to online resources. They even share, discuss, chat, resources, which magnifies their learning. They take up assessments online, get instant feedback about their performance, and work on improvement.
Student experience expands, their engagement levels skyrocket and their learning experience gets interesting.
Computational thinking
This is a way of solving real-life problems by designing systems. Students apply real-world contexts to the lessons they learn, which increases engagement levels.
Experiential or Expeditionary learning
This is the most wanted skill according to Education 4.0. It’s all about building student autonomy. This is learning through doing or “hands-on” experience and it is popular across the world. With experiential learning or discovery learning pedagogy, the shift in learning happens from teacher-centered to teacher-facilitated, with students learning from ‘doing’ experiences.
Students take complete responsibility in their learning process, self-reflect, and improve. They are an active participant in the learning process and not a disengaged onlooker.
Embodied learning
This pedagogy involves intellect and body to come together in promoting the active engagement of children in the classroom. Students put to use skills including mathematical, creative, and problem-solving to construct complex structures. Embodied learning helps students learn with confidence and create better learning outcomes.
Personalized Learning
This high-tech pedagogy method is still evolving. It has students’ choices and self-direction as its hallmark. Personalized learning has always been the students’ favorite as it places students at the center. With the assessments and assignments that are tailored to the students, a competency-based progression happens, where students move to the next topic upon mastering the current one.
With the pedagogical tools in CBE, there’s a place for more career readiness with self-learning environments. Students who don’t require remediation or extension work can instead work with teachers to nurture social skills and other or 21st-century skills lessons and receive mentoring.
Personalized learning mostly comes with virtual platforms, online lessons, and programs, so faculty should be adaptable to using the technology with ease and comfort.
Inquiry-based Learning
Again a high-tech pedagogy, inquiry-based learning is more of students’ investigation and ability to work on projects and needs a faculty as a support to give guidance and support. This method of instruction may have faculty as facilitators, personal models, and delegators.

Technology can help inquiry-based learning to a larger extent with the online ways of learning, researching, social media, and expanding global connections with people all over the world.
Benefits of pedagogical tools during Covid
Self-reflection
Students nurture higher-order thinking. By infixing Bloom’s and Solo’s taxonomy levels of teaching in learning, students easily develop critical thinking skills in both abstract and conceptual terms. They self-reflect by applying strategies in the complex situations that they deal with.
Improves critical thinking
Students in the digital age develop critical skills like Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Making the use of pedagogy tools for discussion forums, video conferencing, and seminars, students can casually collaborate with their peers, do collaborative research, respond to their queries, and get instant insights.
Fosters intellectual development through collaboration
There’s always an advantage for intellectual development through probing, collaboration, and working together.
Pedagogical assessment tools
Modern pedagogy needs modern assessment tools, especially to assist the times like Covid.
Prior to assessing students, faculty are supposed to set clear and transparent objectives, involve students in self and peer assessment, and give timely and appropriate feedback.
Unlike the traditional way, assessments were conducted, there are online tools to conduct OBE-based assessments with online proctoring features, auto-device shutdown, auto-shuffling of questions, rubrics-assisted formative assessments, peer assessment, classroom polling, quizzes, surveys, etc.
Interactive pedagogical tools that Creatrix offers during Covid
- Self-learning
- Peer learning
- Student community
- Virtual class enablement
- Interactive video & audio
- Assessment and Assignment review
- Inbuilt quizzes
- Video learning / Live Session Integration
- Automated feedback
- Discussions through forums, activity walls, polling
- There are inbuilt quizzes, discussion forums, virtual class enablement, learning outcomes mapping, and much more!
Contact us to know more information about how we assist active learning through modern pedagogical learning.



