20-Step Guide for Implementing the Outcome-Based Education (OBE) Process
In a fast-paced educational realm, Outcome-Based Education (OBE) emerges as the catalyst for student success. According to a recent survey by the Association of American Colleges and Universities, institutions adopting OBE witness a remarkable 25% increase in student engagement and a transformative 15% surge in graduation rates. It also leads to a 20% boost in institutional effectiveness, fostering a dynamic learning environment. Higher education institutions have started raving about the practical adoption of Outcome Based Education within their campuses. The buzz revolves around the anticipated positive outcomes that can result from embracing this approach. To assist those keen on Outcome-Based Education but unsure of the process, this blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide, breaking down the 20 essential steps for successful implementation in your educational space.
OBE Implementation Process - 20 Big Steps
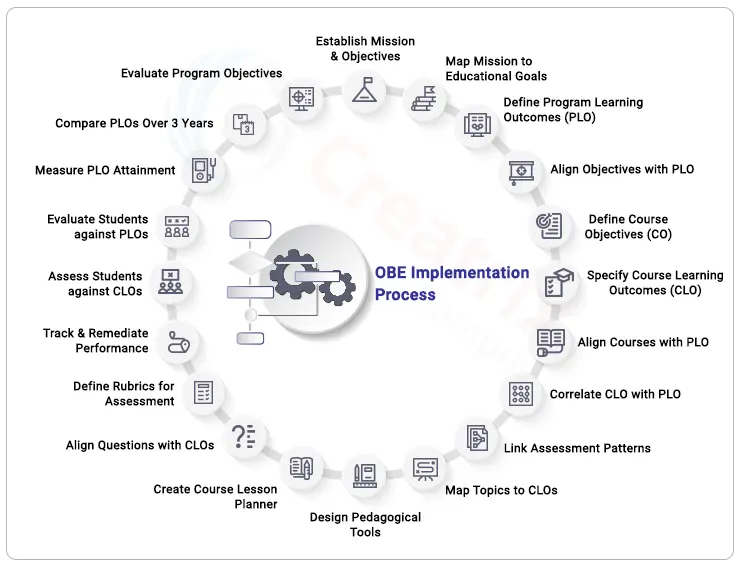
Embarking on the journey of implementing an Outcome-Based Learning Framework requires a strategic approach and meticulous planning. Navigating the implementation of an Outcome-Based Learning Framework is simplified with the expertise of Creatrix Campus. The following section not only provides a foundational understanding but also introduces the carefully curated 20 pivotal steps crafted by our experts. These steps are designed to guide you seamlessly through the process, ensuring a successful adoption of the Outcome-Based Education model in your educational institution.
- Establish Mission statements, Program Educational Objectives
- Map Mission Statements with Program Educational Objectives (PEOs)
- Define PLO with Bloom's Taxonomy
- Map Program Educational Objectives with PLO
- Define CO (Course Objectives)
- Define CLO (Course Learning Outcomes) with Bloom’s Taxonomy for each Course
- Map Courses with PLO at suitable levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Map CLO with PLO at suitable levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Map Assessment Pattern with CLO of each course
- Map Topics with CLOs
- Define pedagogical tools for course outcomes delivery
- Preparing session-wise Course Lesson Planner
- Map Questions with CLOs at Bloom’s Taxonomy levels & Assessments
- Define rubrics with Bloom’s Taxonomy and CLO
- Track students' performance by proposing proper remedial measures
- Measure students' performance against CLO threshold, course-wise
- Measure students' performance against the PLO threshold, semester-wise
- Measure the attainment of each PLO through Direct/Indirect assessments
- Compare PLO for the last 3 academic years and propose remedial actions
- Assess the attainment of Program Educational Objectives
1. Establishing Mission Statements, Program Educational Objectives
Begin the journey by establishing clear mission statements and defining Program Educational Objectives (PEOs). This foundational step sets the tone for your institution's commitment to Outcome-Based Education, providing a roadmap for educational success. To achieve the same, you could try the following suggestions;
- Engage key stakeholders in collaborative discussions on institutional values and goals.
- Facilitate workshops to articulate a unique mission statement that defines your institution.
- Ensure Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) align with the mission and adhere to SMART criteria.
- Try automating this process with Creatrix Campus Strategic Planner software. Involve subject matter experts in defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound PEOs.
- Leverage Creatrix Campus expertise for guidance on best practices in crafting mission statements and PEOs.
2. Mapping Mission Statements with Program Educational Objectives
To align mission statements with Program Educational Objectives (PEOs), start by thoroughly reviewing the institution's mission statements. Identify key themes or values emphasized in the mission, and then determine how these themes relate to specific academic programs. Articulate Program Educational Objectives that align seamlessly with the institution's overarching mission.
Suggestions:
- Hold collaborative sessions involving academic and administrative staff.
- Use visual aids like mind maps to illustrate connections.
- Regularly revisit and revise objectives based on mission changes.
3. Defining Program Learning Outcomes with Bloom's Taxonomy
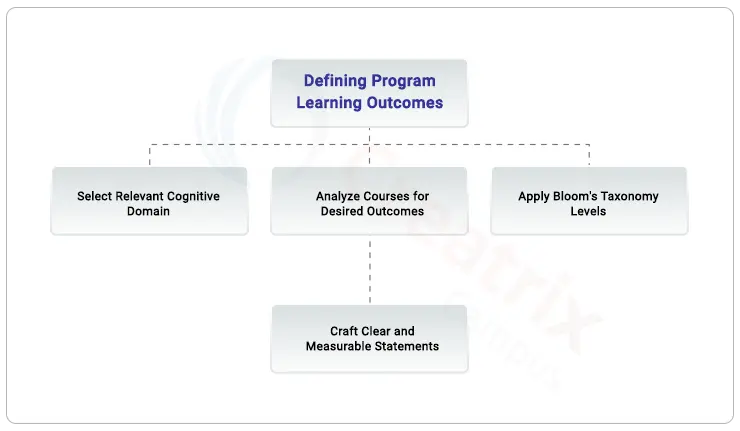
When defining Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) using Bloom's Taxonomy, first, select the relevant cognitive domain for the outcomes. Analyze courses within the program to identify desired learning outcomes and then apply Bloom's Taxonomy levels to each outcome. Craft clear and precise statements that are measurable and aligned with program goals.
Suggestions:
- Conduct faculty workshops on the application of Bloom's Taxonomy.
- Encourage faculty collaboration for outcome definition.
- Incorporate real-world scenarios into outcome descriptions for clarity.
4. Mapping Program Educational Objectives with Program Learning Outcomes
Connect Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) and Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) directly. See how achieving PEOs contributes to reaching PLOs. This helps maintain a clear and organized education structure.
Suggestions:
- Use matrices to visually map PEOs and PLOs for a clearer understanding.
- Talk with faculty members to comprehensively map the connection between PEOs and PLOs.
- Keep mappings up-to-date by reviewing them regularly to accommodate any changes.
5. Defining Course Objectives for Each Course
Outline distinct Course Objectives for each academic course that actively contribute to the broader Program Learning Outcomes. Tailor these objectives to fit each course's unique characteristics and goals, offering a clear guide for both instructors and students.
Suggestions:
- Collaborate with subject matter experts to outline course-specific objectives.
- Ensure that course objectives align with overall program goals.
- Consider diverse teaching methods to address varied course objectives.
6. Defining Course Learning Outcomes with Bloom’s Taxonomy and Threshold for Each Course
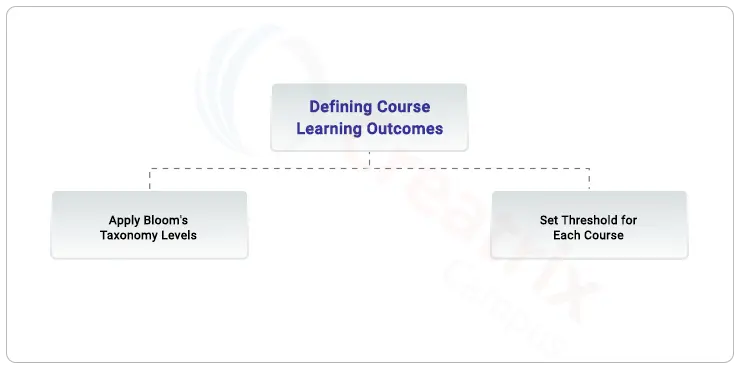
Using Bloom's Taxonomy, define Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) for each course. Incorporate a threshold level to signify the minimum acceptable standard for achievement. This step ensures clarity in expectations and provides a framework for assessing student performance.
Suggestions:
- Conduct faculty development sessions on Bloom's Taxonomy application.
- Establish a consensus on threshold levels for objective evaluation.
- Integrate practical scenarios into CLOs for contextual understanding.
7. Map Courses with PLOs at Suitable Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Establish a connection between courses and Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) by mapping them at appropriate Bloom’s Taxonomy levels. This ensures that the cognitive demands of each course align with the overall program objectives, fostering a harmonized educational experience.
Suggestions:
- Collaborate with faculty members to identify the cognitive complexity of each course.
- Use visual aids, such as matrices, for clear mapping representation.
- Regularly review and update mappings to accommodate curriculum changes.
8. Map CLO with PLO at Suitable Levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Ensure a seamless alignment between Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) and Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) by mapping them at suitable Bloom’s Taxonomy levels. This process strengthens the connection between specific course objectives and broader program goals.
Suggestions:
- Encourage interdisciplinary discussions to enhance mapping accuracy.
- Utilize technology for dynamic mapping adjustments based on assessment results.
- Conduct periodic reviews to validate the relevance of CLO-PLO mappings.
9. Map Assessment Pattern with CLO of Each Course
Align the assessment pattern of each course with Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs). This mapping ensures that assessments effectively measure the targeted learning outcomes and provide valuable insights into student performance.
Suggestions:
- Design varied assessment formats to holistically evaluate CLOs.
- Provide training to faculty on creating assessments aligned with learning objectives.
- Implement a feedback loop for continuous improvement in assessment strategies.
10. Map Topics with CLOs
Forge a direct link between the subjects covered in a course and the Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) to enrich the significance of the content and foster a more profound grasp of the learning objectives.
Suggestions:
- Inspire faculty to infuse real-world examples into the mapped topics.
- Cultivate collaborative discussions exploring the intricate connections between topics and CLOs.
- Keep mappings dynamic by consistently updating them to mirror changes in course content or objectives, ensuring continual alignment with evolving educational requirements.
11. Define Pedagogical Tools for Course Outcomes Delivery
Specify pedagogical tools and methodologies that align with the delivery of Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs). This step ensures that the chosen teaching methods effectively support the achievement of targeted learning objectives.
Suggestions:
- Provide faculty development programs on diverse pedagogical approaches.
- Encourage experimentation with innovative teaching tools.
- Facilitate peer discussions to share successful pedagogical practices.
12. Preparing Session-Wise Course Lesson Planner
Streamline the teaching process by developing a session-wise course lesson planner. This detailed plan ensures that each session is purposefully designed to achieve specific Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs), contributing to a cohesive and structured curriculum.
Suggestions:
- Include active learning strategies in lesson plans to enhance student engagement.
- Emphasize flexibility in lesson planning to accommodate unexpected shifts in the academic calendar.
- Encourage faculty collaboration in creating standardized lesson planning templates.
13. Map Questions with CLOs at Bloom’s Taxonomy Levels & Assessments
Align assessment questions with Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs) using Bloom’s Taxonomy levels. This mapping ensures that questions reflect the cognitive complexity intended for each outcome, facilitating a more nuanced evaluation of student understanding.
Suggestions:
- Provide faculty training on constructing questions aligned with Bloom’s Taxonomy.
- Foster a question bank for efficient assessment creation.
- Implement a systematic approach to assess the effectiveness of mapped questions.
14. Define Rubrics with Bloom’s Taxonomy and CLO
Enhance assessment clarity by defining rubrics aligned with Bloom’s Taxonomy and Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs). This step ensures standardized and transparent evaluation criteria, promoting consistency and fairness.
Suggestions:
- Conduct workshops on rubric creation and application.
- Foster collaborative discussions on refining and improving rubrics.
- Regularly update rubrics to reflect changes in course content or objectives.
15. Track Students’ Performance by Proposing Proper Remedial Measures
Implement a robust tracking system to monitor students’ performance based on Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs). Propose timely remedial measures to address any identified gaps and ensure continuous improvement.
Suggestions:
- Utilize data analytics tools for efficient performance tracking.
- Facilitate regular feedback sessions to discuss performance trends.
- Encourage faculty to proactively suggest and implement remedial actions.
16. Measure Students’ Performance Against CLO Threshold, Course-Wise
Establish a quantitative measurement of students’ performance against Course Learning Outcome (CLO) thresholds on a course-by-course basis. This provides a granular understanding of achievement levels, guiding further instructional strategies.
Suggestions:
- Define clear threshold criteria for each CLO.
- Implement a user-friendly dashboard for visualizing performance metrics.
- Regularly review and adjust threshold levels based on student performance trends.
17. Measure Students’ Performance Against PLO Threshold, Semester-Wise
Expand the evaluation of student performance to the Program Learning Outcome (PLO) level, assessing achievements against set standards on a semester basis. This comprehensive assessment offers valuable insights into the curriculum's overall effectiveness.
Suggestions:
- Work with faculty to set semester-wise PLO standards for assessment.
- Conduct regular reviews to maintain the relevance and accuracy of PLO measurements.
- Incorporate feedback from industry experts to enhance and fine-tune the criteria for PLO thresholds.
18. Measure the Attainment of Each PLO Through Direct/Indirect Assessments
Implement a comprehensive assessment strategy to measure the attainment of each Program Learning Outcome (PLO) through both direct and indirect assessments. This dual approach provides a multifaceted understanding of PLO achievement.
Suggestions:
- Design a mix of direct and indirect assessment methods for PLO evaluation.
- Leverage external stakeholders for indirect assessment feedback.
- Regularly update assessment strategies to align with evolving PLO objectives.
19. Compare PLO for the Last 3 Academic Years and Propose Remedial Actions
Perform a retrospective analysis by comparing Program Learning Outcome (PLO) data from the past three academic years. Using this comparison, suggest strategic remedial actions to address any areas for improvement.
Suggestions:
- Utilize data visualization tools for a detailed trend analysis.
- Foster collaborative discussions on the recommended remedial actions.
- Implement a continuous improvement cycle based on the findings of the assessment.
20. Assess the Attainment of Program Educational Objectives
Evaluate how well Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) are met by combining data from Program Learning Outcome (PLO) assessments. This final step gives a complete picture of the overall achievement of educational goals.
Suggestions:
- Create a simple process for evaluating PEOs systematically.
- Regularly talk with academic and industry stakeholders for well-rounded feedback.
- Adjust PEOs based on the ongoing improvement process.
Navigate Future with Creatrix Campus OBE Implementation Process
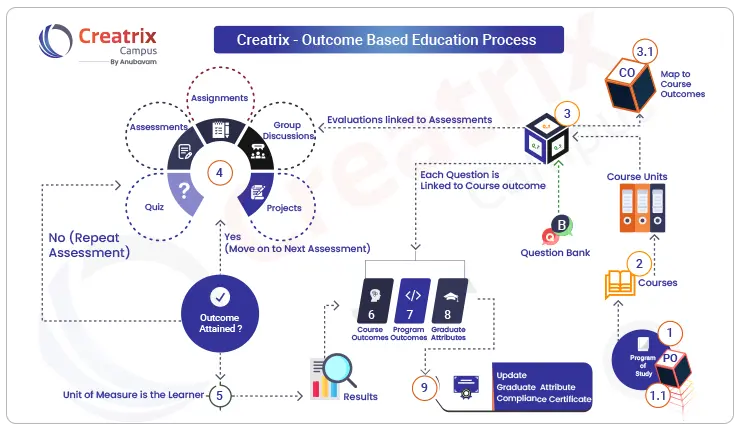
The journey towards Outcome-Based Education (OBE) unfolds as a catalyst for positive change within higher education institutions. As we've navigated through the 20 crucial steps, it's evident that OBE promises enhanced educational outcomes and a refined learning experience.
Unlocking the potential of Outcome-Based Education doesn't just transform classrooms; it has far-reaching implications for institutional success. Decision-makers in higher education are increasingly recognizing the advantages, not just in terms of improved learning outcomes but also in terms of Return on Investment (ROI) and strategic alignment.
To streamline and automate the end-to-end OBE process with an eye on ROI, consider leveraging Creatrix Campus. With its cutting-edge technology and expertise in Outcome-Based Education, Creatrix Campus offers a seamless solution for institutions aspiring to integrate OBE effectively. From establishing mission statements to evaluating Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) and Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs), Creatrix Campus provides a unified platform for holistic OBE implementation.
If you are ready to transform your educational space with Outcome-Based Education, contact our team now!


